Compass Sensor
High Precision Compass Sensor, 2D, 0-360°
Electronic Compass Sensor with Magnetic, 3D, 0°-180°
3D E Compass Sensor, RS485/RS232/TTL
Compass Sensor, Pitch ±90°, Roll 360°
Electronic Compass Sensor, 3D, RS485/RS232/TTL
Electronic Compass Module, 2D, 0°-360°
3D Electronic Compass Module with Magnetic, RS232
Digital Compass Sensor, Bluetooth 50m
Working Principle
A compass sensor operates based on the principle of measuring the Earth’s magnetic field vector to determine orientation and heading. It typically integrates a three-axis magnetometer with auxiliary sensors such as accelerometers and gyroscopes to perform sensor fusion. Through calibration methods, it eliminates hard-iron and soft-iron interference, compensates for tilt angles, and corrects errors caused by temperature drift and electromagnetic disturbances. By processing these signals, the compass sensor calculates Euler angles, enabling accurate heading and orientation detection in both static and dynamic environments.
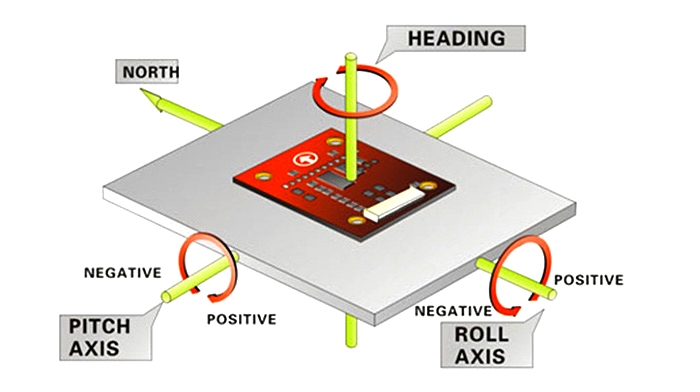
Detection and Compensation Methods
The sensor employs multiple detection techniques to ensure reliability. Magnetic field calibration is performed by rotating the sensor, compensating interference using dipole field models. Heading accuracy is verified by comparing measured values on a non-magnetic turntable against standard angles. Tilt compensation uses gravity acceleration components to adjust for inclined installation. Temperature drift is tested from -40℃ to +85℃, and real-time temperature sensors provide compensation. Electromagnetic interference resistance is evaluated using Helmholtz coils to simulate magnetic disturbances, while noise suppression is achieved through spectral analysis and digital filtering. Dynamic response testing measures delay under rapid rotation, ensuring fast and stable output in mobile applications.
Types of Compass Sensors
Compass sensors are available in several types depending on their design and integration.
- 2D Compass Sensors: Measure horizontal heading only, suitable for flat installations.
- 3D Compass Sensors: Integrate three-axis magnetometers and accelerometers, capable of measuring heading, pitch, and roll angles.
- Electronic Compass Modules: Provide digital interfaces such as RS232, RS485, or TTL, and often include tilt and magnetic compensation for industrial and automotive systems.
- Integrated MEMS Compasses: Combine magnetometers with gyroscopes and accelerometers in a compact chip, widely used in consumer electronics, UAVs, and robotics.
Applications
Compass sensors are widely applied across different industries. In marine navigation, they provide heading reference for ships and underwater vehicles. In automotive systems, they assist with vehicle navigation, electronic stability control, and advanced driver assistance systems. In unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and robotics, they enable precise orientation and path planning. In geophysical instruments and surveying equipment, they ensure accurate alignment and measurement. Additionally, compass sensors are used in antenna stabilization, portable electronics, and industrial automation, where stable and reliable orientation data is essential.

Other Features and Advantages
Modern compass sensors are compact, lightweight, and energy-efficient, with power consumption as low as a few milliamps, making them ideal for embedded applications. They support wide operating temperature ranges and feature strong vibration resistance for use in harsh environments. With digital output formats and multiple communication protocols, they are easily integrated into existing systems. Furthermore, advanced calibration, temperature compensation, and filtering algorithms enhance stability, ensuring accurate operation even in environments with strong electromagnetic interference.
























